In industrial applications, both AC and DC motorsare used to provide power. Although DC motors evolved from AC motors, there are significant differences between the two motor types that can affect the performance of your equipment. Therefore, it is important for industrial customers to understand these differences before selecting a motor for their application.
AC Motors: These motors use alternating current (AC) to generate mechanical energy from electrical energy. The design of any type of AC motor is the same - they all contain a stator and a rotor. The stator generates a magnetic field, and the rotor rotates due to the induction of the magnetic field. When selecting an AC motor, two important characteristics to consider are operating speed (RPMS) and starting torque.
DC Motor: A DC motor is a mechanically commutated machine that utilizes direct current (DC). They consist of rotating armature windings and permanent magnets which act as static magnetic fields. These motors use a static field and armature winding connections to produce varying speeds and torque levels. Unlike AC motors, the speed of DC motors can be controlled by varying the voltage applied to the armature or by adjusting the static field current.

AC motors and DC motors:
AC motors run on alternating current, while DC motors use direct current. A DC motor receives power from a battery or battery pack that provides a constant voltage, allowing electrons to flow in a single direction. The AC motor takes power from the alternator, causing the electrons to change the direction of their flow. The steady energy flow of DC motors makes them ideal for applications that require consistent speed, torque, and operation. AC motors have continuous energy change and are ideal for industrial and residential applications. AC motors are preferred for compressor power drives, air conditioning compressors, hydraulic pumps and irrigation pumps, while DC motors are preferred for steel mill rolling equipment and paper machines.
Which Motor Is More Powerful: AC or DC?
AC motors are generally considered to be more powerful than DC motors because they can generate higher torque by using a more powerful current. However, DC motors are typically more efficient and make better use of their input energy. Both AC and DC motors come in a variety of sizes and strengths that can meet any industry’s power requirements.
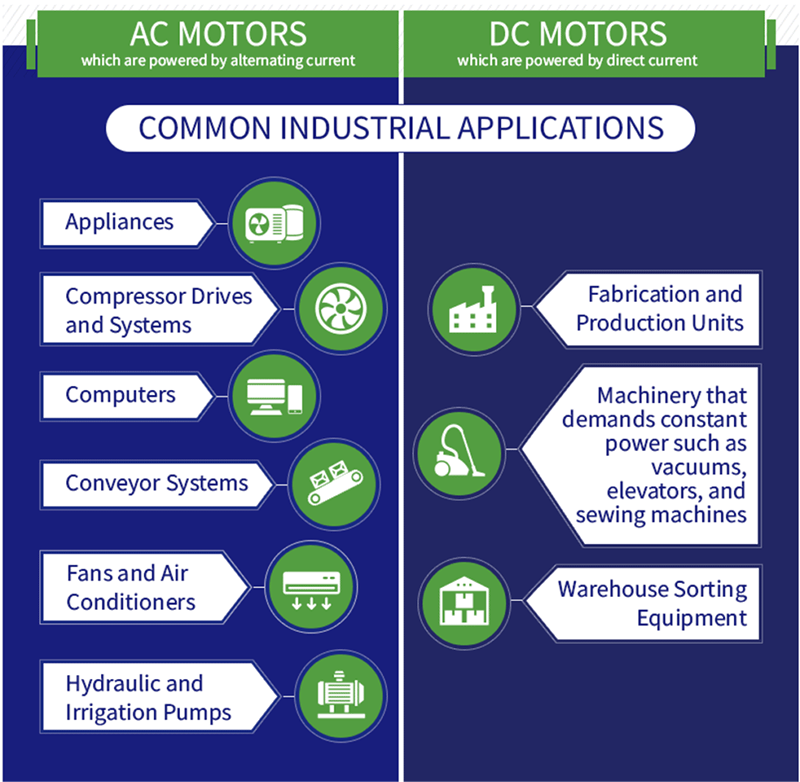
Factors to consider:
Power supply and power control levels are key factors that customers need to consider for AC and DC motors. When selecting a motor, it is best to consult a professional engineering organization. They can learn more about your application and suggest the right type of AC and DC motor repair solution based on your requirements.
Post time: Apr-26-2023
